CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME or median neuropathy at the wrist, is a medical condition in which the median nerve is compressed at the wrist leading to paresthesia numbness, pain and muscle weakness in the hand.It is caused by an inflammation or collapse of carpal tunnel that allows nerves to passes through the wrist.It is a common complaint of office workers,drivers and is usually associated with repetitive activities such as typing,etc.Because the nerves of the tunnel run through the neck and arms before reaching the wrist.Tension in the neck and shoulders can also aggravate the condition.Some predisposing factors like diabetics, pregnancy, hypothyroidism, and heavy manual work or work with vibrating tools may also cause the symptoms.
Anatomy of wrist:
For understanding more about CTS, it is important to know the part of the hand wrist.
 |
| anatomy of wrist |
The Carpal Tunnel: The carpal tunnel is a passageway that forms beneath the strong, broad transverse ligament. This ligament is a bridge that extends across the lower palm and connects the bones of the wrist (carpals) that form an arch below the tunnel.
The Median Nerve and Flexor Tendons: The median nerve and nine flexor tendonspass under the ligament bridge and through the carpal tunnel (similar to a river). They extend from the forearm and up into the hand:
- The flexor tendons are fibrous cords that connect the muscles in the forearm to the fingers (two to each finger) and one to the thumb. They allow flexing of the fingers and clenching of the fist.
- The median nerve plays two important roles. It supplies sensation to the palm to side of the thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers, and to the flexor tendons. It provides function for the muscles at the base of the thumb (the thenar muscle).
The median nerve travels through a compartment in the wrist called the carpal tunnel. The ligaments that transverse the nerve are not very flexible. Any swelling within the wrist compartment can put excessive pressure on structures such as the blood vessels and the median nerve. Excessive pressure can constrict blood flow and cause nerve damage. The symptoms from the compression cause pain, loss of sensation, and decreased function in the hand.
Symptoms:
The level of discomfort varies from a simple dull ache to complete numbness of the hand.Symptoms starts with mild discomfort or pain in the wrist region and slowly spreads to the hand and fore arm.The first symptoms of CTS may appear while sleeping and typically include numbness and paresthesia (burning and tingling sensation),in the thumb ,index and middle finger. Some patients express the symptoms as well.Symptoms of CTS usually progress gradually over weeks and months ,and sometimes years.
 |
| symptoms |
- Tingling and burning sensation of the hand.
- wrist pain that often shoots up till the elbow and at times up till the shoulder.
- clumsiness caused by sense of weakness only in the affected hand.
- Difficulty or lose of finger coordination and movement.
- weak grip.
- weakness in the hand.
- Pin increase during driving,doing job and also at night.
- frequency accompanied by sharp pains radiating through arm.
 |
| thenar muscle wasting |
- wasting of thenar muscles (muscles which connected to the thumb.
- weakness of palmar abduction of the thumb(difficulty bringing the thumb away from the hand).
- symptoms are usually worse at night and after prolonged use of the hand.
- Decreased grip,unable to tell cold and hot in touch.
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
CTS can be the result of overuse,strain,forceful or stressed motions of hand and wrists.Clinically IT professionals, architects and computer users are reported to have this condition in high numbers compared to common people. Incidence in women is as much as 3 times higher than in men.
- work related.
- high force and vibrations: work that involves high force or vibrations as is repetitive hand and wrist work in cold temperature.
- hand arm vibrations syndrome- tingling and numbness that present even after the vibration stops.
- typing for prolonged period on the keyboard.
- driving continuously.
- playing a hand dominated musical instrument and sports.
- Sewing,writing for a prolonged period.
- improper sitting in front of computer.
- improper use of key board and mouse.
Risk factors of Carpal tunnel Syndrome:
- Age: older peoples are at very higher risk than younger.
- Sex: women have more risk than men,especially at a time like pregnancy,after delivery,menopause,etc
- Obesity and lack of fitness.
- Very High-Risk Workers. Workers in the meat and fish packing industries and those who assemble air planes have the highest risk for CTS
- Computer Users and Typists. Repetitive typing and key entry has traditionally been associated with missing work due to CTS (as opposed to repetitive stress symptoms, which are unrelated to nerve impingement).
- Musicians. Musicians are at very high risk for CTS and other problems related to the muscles and nerves in the hands, upper trunk, and neck.
- Smoking and Alcoholism: Cigarette smoking slows down blood flow, so that smokers have worse symptoms and slower recovery than nonsmokers do. Increased alcohol intake has been associated with CTS in people with other risk factors.
- Poor nutrition,etc
How to Diagnose:
Carpal tunnel syndrome are diagnosed based on the symptoms and the distribution of the hand numbness,pain,nocturnal symptoms,thenar muscle wasting, etc.Examine the wrist for any swelling,warmth,tenderness deformity,etc.Examine the neck,shoulder,pulse,etc to exclude other conditions.
one diagnostic key is if the numbness in the finger does not include the little finger.The median nerve does not provide sensation to this finger.
Test strength of the muscles of the hand,thumb,fingers,etc.Each finger should be tested for sensation and the muscles at the base of the hand should be examined for strength and signs of atrophy.
The following findings are helpful in identifying carpal tunnel syndrome:
Studies suggest that surgery is a better option for severe CTS. Surgery is also more likely to be necessary for patients with underlying conditions such as diabetes. Even among patients with mild CTS, there is a high risk of relapse. Some researchers are reporting better results when specific exercises for carpal tunnel syndrome are added to the program of treatments.
Limiting Movement. If possible, the patient should avoid activities at work or home that may aggravate the syndrome. The affected hand and wrist should be rested for 2 - 6 weeks. This allows the swollen, inflamed tissues to shrink and relieves pressure on the median nerve. If the injury is work related, the worker should ask to see if other jobs are available that will not involve the same hand or wrist actions. Few studies have been conducted on ergonomically designed furniture or equipment, or on frequent rest breaks. However, it is reasonable to ask for these if other work is not available.
Conservative Treatment Approach. The following conservative approaches have been shown to provide symptom relief:
Underlying Conditions. It is important to treat any underlying medical condition that might be causing carpal tunnel syndrome. For example, reducing inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis or other forms of inflammatory disorders that directly cause CTS is very helpful. Hypothyroidism and diabetes are diseases associated with an increased risk of CTS. The treatments for such diseases may offer some relief for CTS symptoms.

Low-Level Laser Therapy. Some investigators are working with low-level laser therapy (LLLT), which generates extremely pure light in a single wavelength. The procedure is painless. Two trials comparing laser therapy to conservative treatment or a placebo laser treatment from no real benefit for this therapy.
Vitamin B6. Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is often used for carpal tunnel syndrome. Studies have not supported its benefits, however, either in oral or cream form. It should also be noted that excessively high doses of vitamin B6 can be toxic and cause nerve damage.
Acupuncture. A very limited amount of evidence shows that acupuncture may be useful as a supplement to standard treatment.
Chiropractic Therapies. Chiropractic techniques have been useful for some people whose condition is produced by pinched nerves. There is little evidence, however, to support its use for carpal tunnel syndrome.
Magnets. Magnets are a popular but unproven therapy for pain relief.
Botulinum toxin type A. Intracarpal injections of botulinum toxin type A (Botox) has not been well studied.
one diagnostic key is if the numbness in the finger does not include the little finger.The median nerve does not provide sensation to this finger.
Test strength of the muscles of the hand,thumb,fingers,etc.Each finger should be tested for sensation and the muscles at the base of the hand should be examined for strength and signs of atrophy.
The following findings are helpful in identifying carpal tunnel syndrome:
- Less sensitivity to pain where the median nerve runs through to the fingers
- Thumb weakness
- Inability to tell the difference between one and two sharp points on the fingertips (this is a late sign of carpal tunnel)
- The patient is asked, "What do you do when your symptoms are worse?"
- If the patient responds with a motion that resembles shaking a thermometer, the doctor can strongly suspect carpal tunnel.
- Can the thumb rise up from the plane of the palm?
- Can the thumb stretch so that its pad rests on the pad of the little finger pad?
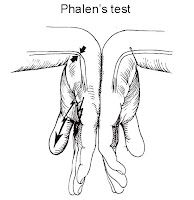
Phalen's test:
Bend wrist and maintain hands in a 90 degree angle,pushing the back of both hands together,for about one minute.If not feel any pain or numbness,then the patient are on the safe level.Actually it is not a definite test to diagnose but help to know the condition.
Tinel's Test:
A classic though less sensitive test is a way to detect irritated nerves. Tinel's is performed by lightly tapping the skin over the flexor retinaculum to elicit a sensation of tingling or "pins and needles" in the nerve distribution. Tinel's sign (pain and/or paresthesias of the median-innervated fingers with percussion over the median nerve) is less sensitive, but slightly more specific than Phalen's sign.
 |
| tinel's test |
Durkan Test:
carpal compression test, or applying firm pressure to the palm over the nerve for up to 30 seconds to elicit symptoms has also been proposed.
 |
| Durkan test |
- Tourniquet Test. This test employs an inflatable cuff that applies pressure over the median nerve to produce tingling or small shocks.
- Hand Elevation Test. The patient raises their hand overhead for 2 minutes to produce symptoms of CTS. The test was recently proven to be accurate and may provide useful information when combined with the Tinel's and Phalen's tests.
Treatments for Carpal tunnel Syndrome:
It is critical to begin treating early phases of carpal tunnel syndrome before the damage progresses. A conservative approach to CTS, which may include corticosteroid injections and splinting, is the first step in treating this disorder. The conservative approach is most successful in patients with mild carpal tunnel syndrome.Studies suggest that surgery is a better option for severe CTS. Surgery is also more likely to be necessary for patients with underlying conditions such as diabetes. Even among patients with mild CTS, there is a high risk of relapse. Some researchers are reporting better results when specific exercises for carpal tunnel syndrome are added to the program of treatments.
Limiting Movement. If possible, the patient should avoid activities at work or home that may aggravate the syndrome. The affected hand and wrist should be rested for 2 - 6 weeks. This allows the swollen, inflamed tissues to shrink and relieves pressure on the median nerve. If the injury is work related, the worker should ask to see if other jobs are available that will not involve the same hand or wrist actions. Few studies have been conducted on ergonomically designed furniture or equipment, or on frequent rest breaks. However, it is reasonable to ask for these if other work is not available.
Conservative Treatment Approach. The following conservative approaches have been shown to provide symptom relief:
- Wrist splints
- Corticosteroids (steroids). Injected or short-term oral corticosteroids may be tried if other methods fail.
Underlying Conditions. It is important to treat any underlying medical condition that might be causing carpal tunnel syndrome. For example, reducing inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis or other forms of inflammatory disorders that directly cause CTS is very helpful. Hypothyroidism and diabetes are diseases associated with an increased risk of CTS. The treatments for such diseases may offer some relief for CTS symptoms.

Wrist Splints
Wrist splints can keep the wrist from bending. They are not as beneficial as surgery for patients with moderate-to-severe CTS, but they appear to be helpful in specific patients, such as those with mild-to-moderate nighttime symptoms of less than a year's duration. In selected patients, up to 80% reported fewer symptoms, usually within days of wearing the splint.
Typically the splint is worn at night or during sports. The splint is used for several weeks or months, depending on the severity of the problem, and may be combined with hand and finger exercises. Benefits may last even after the patient stops wearing the splint.
Other Conservative Approaches
Ice and Warmth. Ice may provide benefit for acute pain. Some patients have reported that alternating warm and cold soaks have been beneficial. (If hot applications relieve pain, most likely the problem is not caused by CTS but by another condition producing similar symptoms.)Low-Level Laser Therapy. Some investigators are working with low-level laser therapy (LLLT), which generates extremely pure light in a single wavelength. The procedure is painless. Two trials comparing laser therapy to conservative treatment or a placebo laser treatment from no real benefit for this therapy.
Alternative Therapies
Many alternative therapies are offered to sufferers of carpal tunnel syndrome and other repetitive stress disorders. Few, however, have any proven benefit. People should carefully educate themselves about how alternative therapies may interact with other medications or impact other medical conditions, and should check with their doctor before trying any of them.Vitamin B6. Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is often used for carpal tunnel syndrome. Studies have not supported its benefits, however, either in oral or cream form. It should also be noted that excessively high doses of vitamin B6 can be toxic and cause nerve damage.
Acupuncture. A very limited amount of evidence shows that acupuncture may be useful as a supplement to standard treatment.
Chiropractic Therapies. Chiropractic techniques have been useful for some people whose condition is produced by pinched nerves. There is little evidence, however, to support its use for carpal tunnel syndrome.
Magnets. Magnets are a popular but unproven therapy for pain relief.
Botulinum toxin type A. Intracarpal injections of botulinum toxin type A (Botox) has not been well studied.


No comments:
Post a Comment